# Using For Loops
# http://10.c1021.fun
### David Rossiter, Gibson Lam and Sung Kim
## Outcomes
### After completing this presentation, you are expected to be able to:
1. Use the range command to make a range of numbers
1. Write loops using the `for` command
## Typical loops
* `n` iterations
* `print` 0 to 9
num = 0
while num < 10:
print (num)
num = num + 1
## Writing Loops Using For
* Previously, we have discussed the use of while loops to do things repeatedly in Python
* In this presentation, we will look at another way of doing loops, using for loops
* Using a for loop:
* perform some actions a particular number of times, or:
* loop through a set of data, performing the same actions on every item in the set
for num in range (1, 10):
print(num)
## For Loops
```
for item in a list of items (range (1, 10)):
. . .statement(s). . .
```
# Sum from 1-9
sum = 0
for i in range (1, 10):
sum = sum + i
print("Sum", sum)
## Do n times
* `range(0, 4)` or `range(4)`
for i in range(4):
print("OK")
## Drawing a Square Using a For Loop
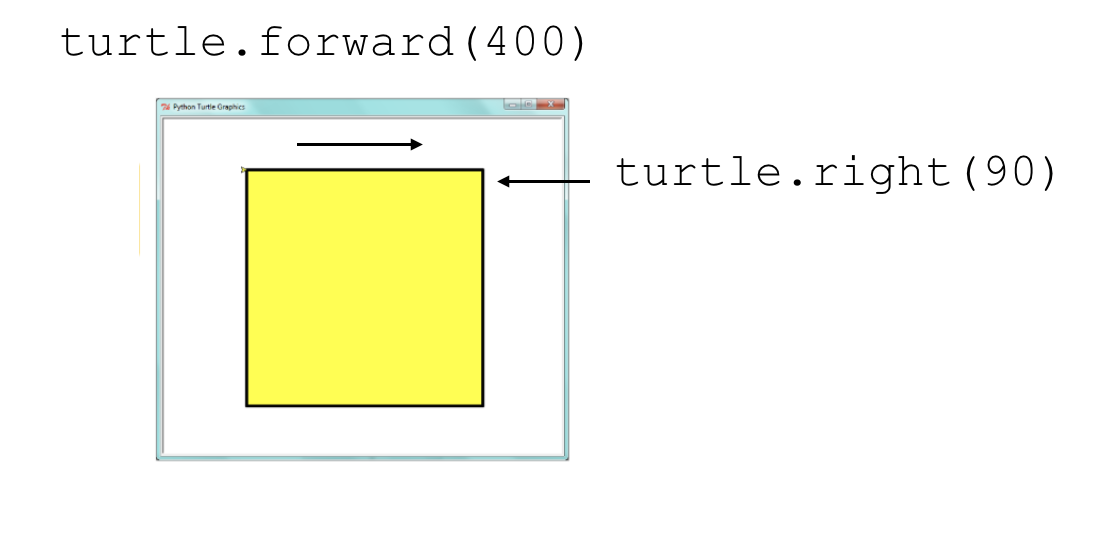
import turtle
for i in range(4):
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.right(90)
## Drawing a Star Shape Using a For Loop
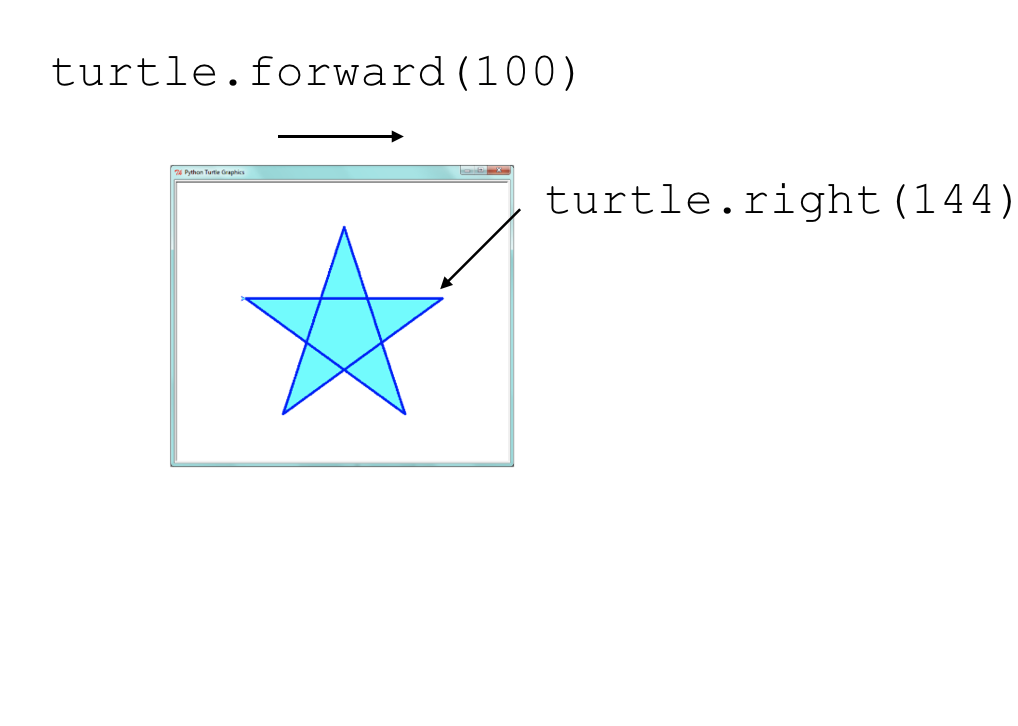
import turtle
for i in range(?):
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.right(144)
## start, end, step
* `range(0, 100, 2)`
* `range(99, 0, -2)`
for i in range(0, 10, 2):
print("I", i)
print("----")
for j in range(9, 0, -2):
print("J", j)
## Spiral Patterns Created Using Turtle
* In the following two examples, patterns are created using for loops and some cleverly chosen numbers
* The turtle draws ‘squares’ using a slightly different angle and a slightly different length for each side
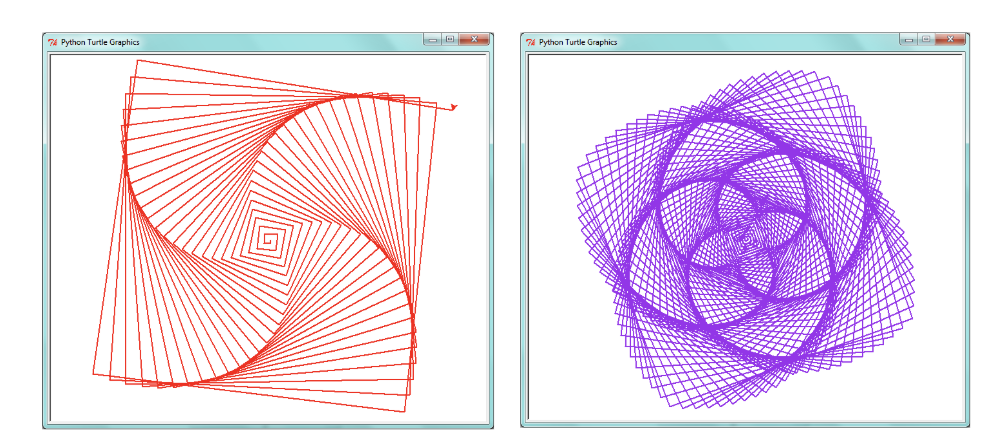
* Start with simple sqares
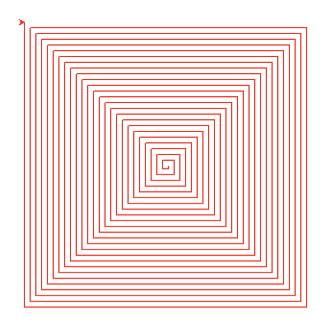
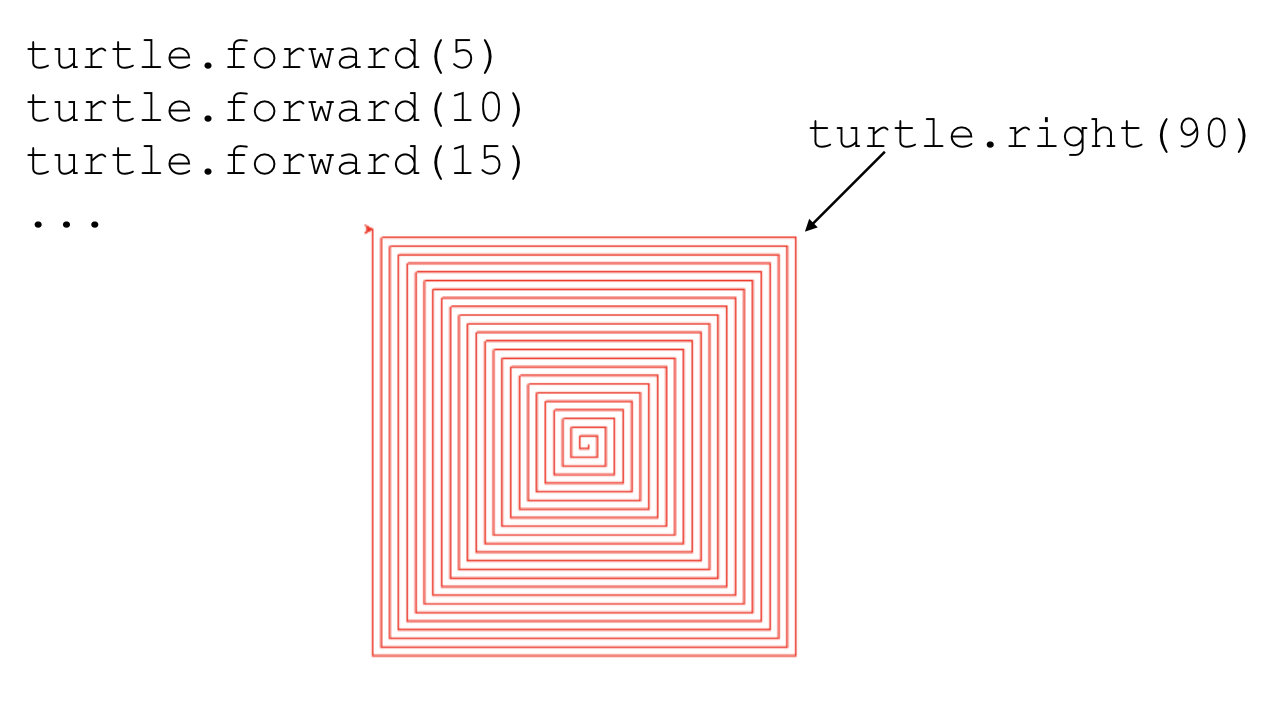
* for loop: 5, 10, 15, ...
* `range (0, 200, 5)`
import turtle
turtle.speed(10)
for i in range(0, 200, 5):
turtle.forward(i)
turtle.right(90)
## Spiral Patterns Created Using Turtle
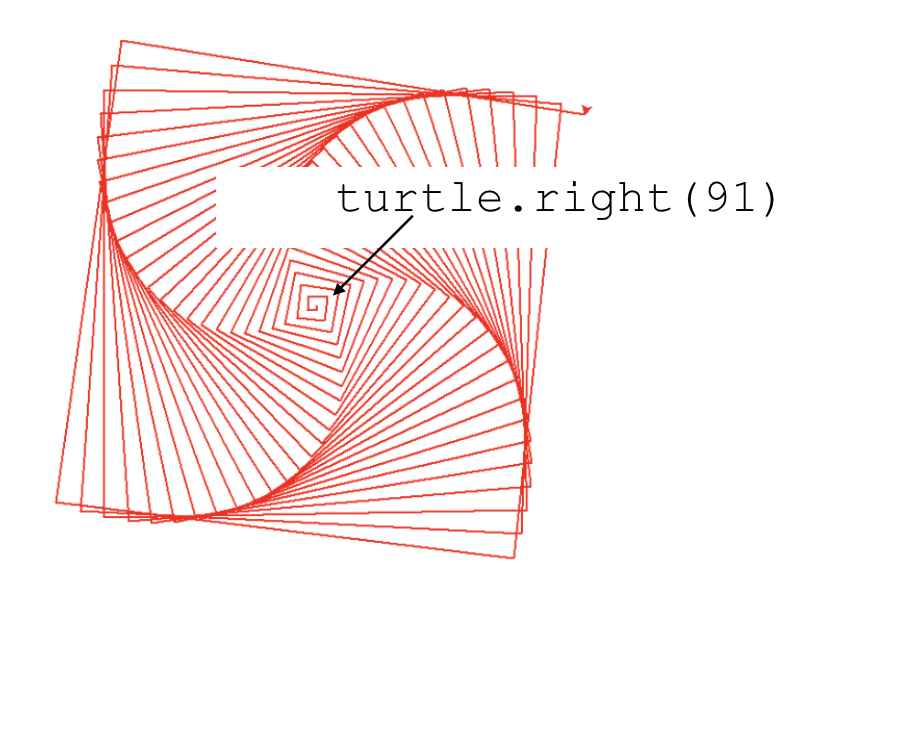
import turtle
turtle.speed(10)
for i in range(0, 300, 3):
turtle.forward(i)
turtle.right(91)
## Flower Spiral Patterns
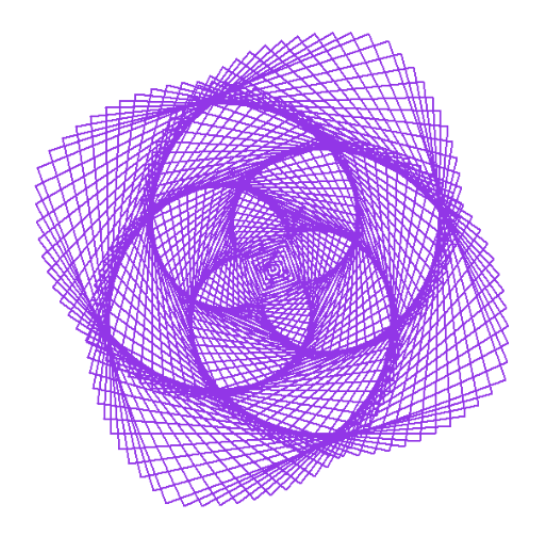
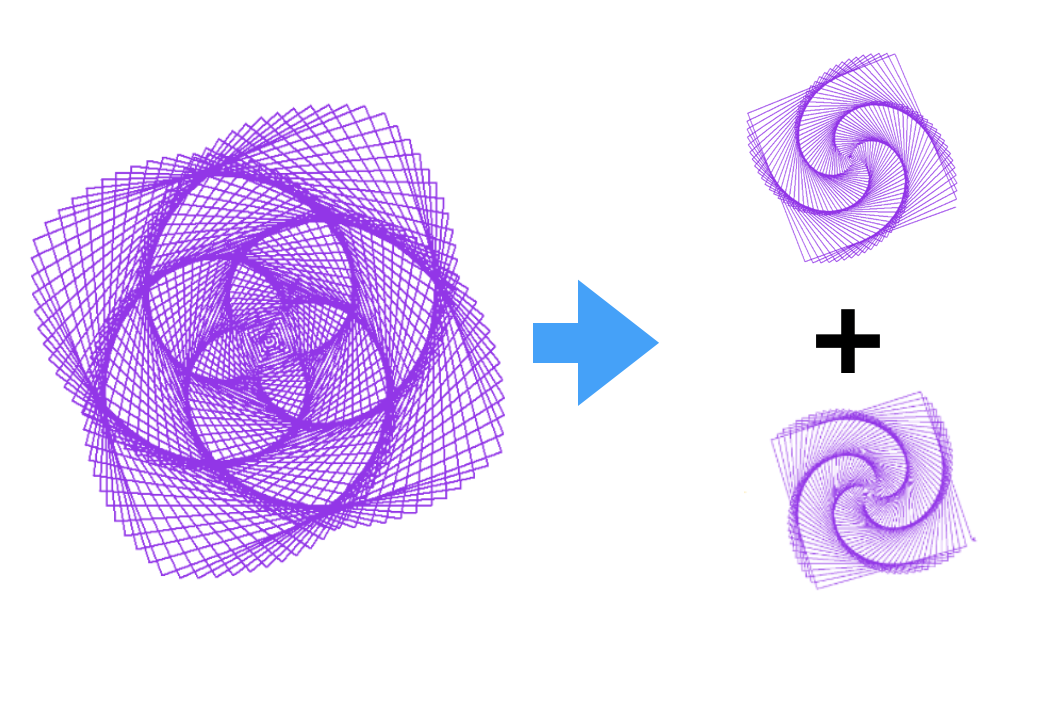
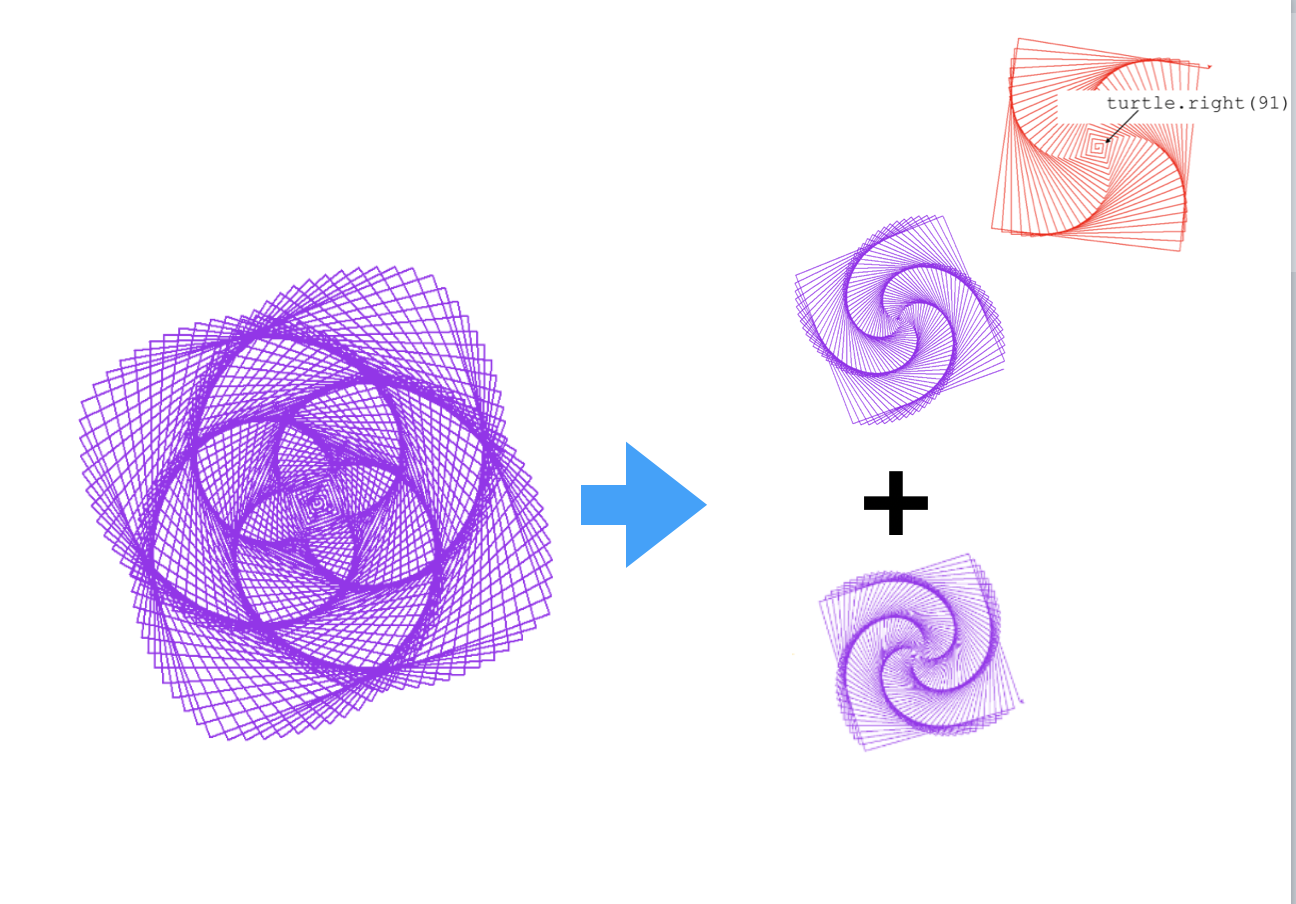
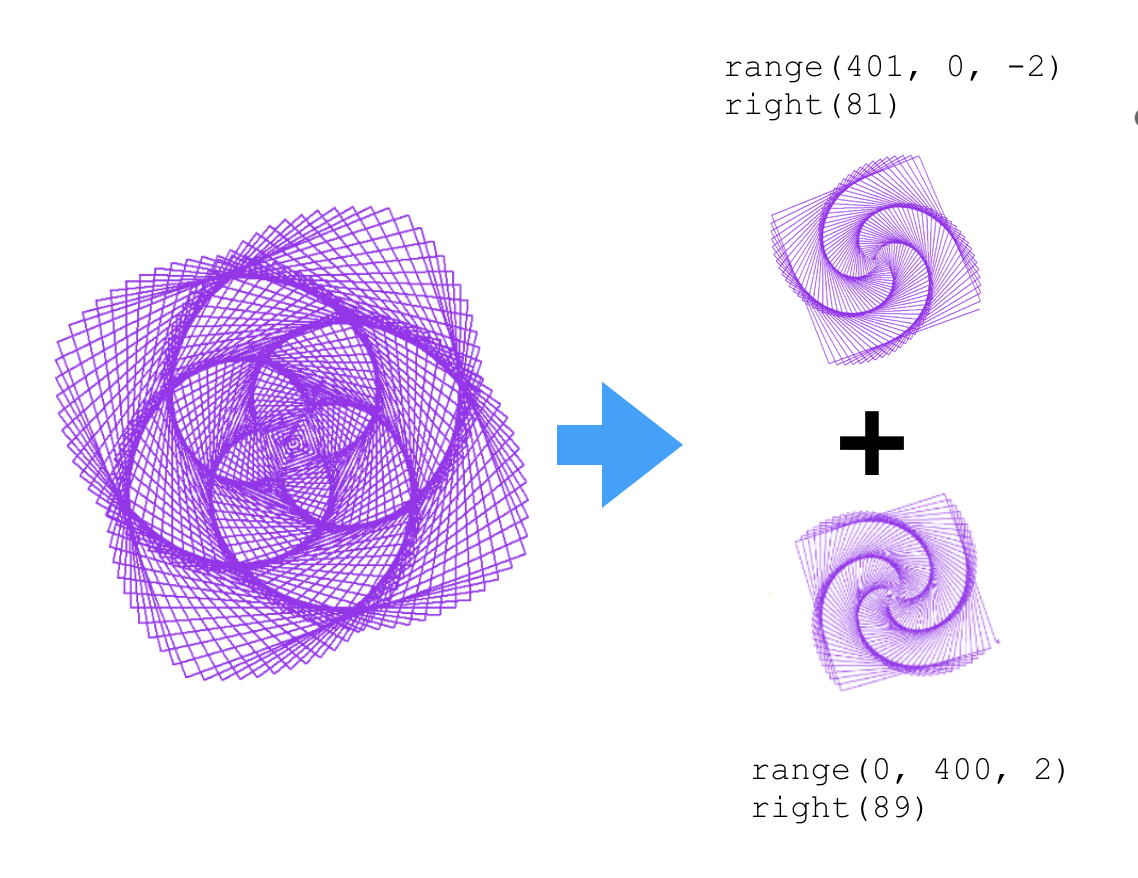
import turtle
turtle.speed(0)
turtle.color('purple')
for i in range(0, 400, 2):
turtle.forward(i)
turtle.right(89)
for i in range(401, 0, -2):
turtle.forward(i)
turtle.right(89)
## Nested for loops
* for loops in side for loops
for i in range(10):
for j in range (10):
print("I & J", i, j)
## Multiplication table
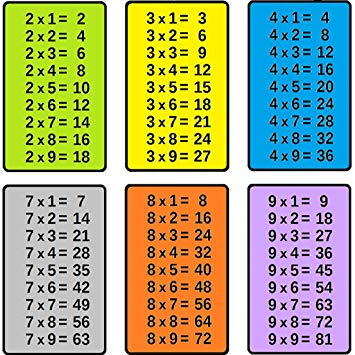
for i in range(2, 10):
for j in range (2, 10):
print(i, "X", j, "=", i * j)
print("---")
## The Flower Pattern Created By Hexagons
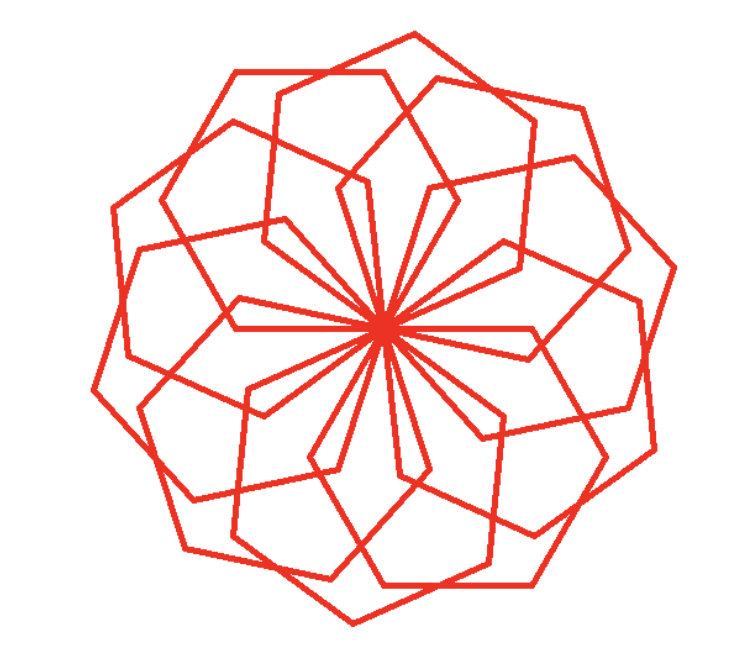
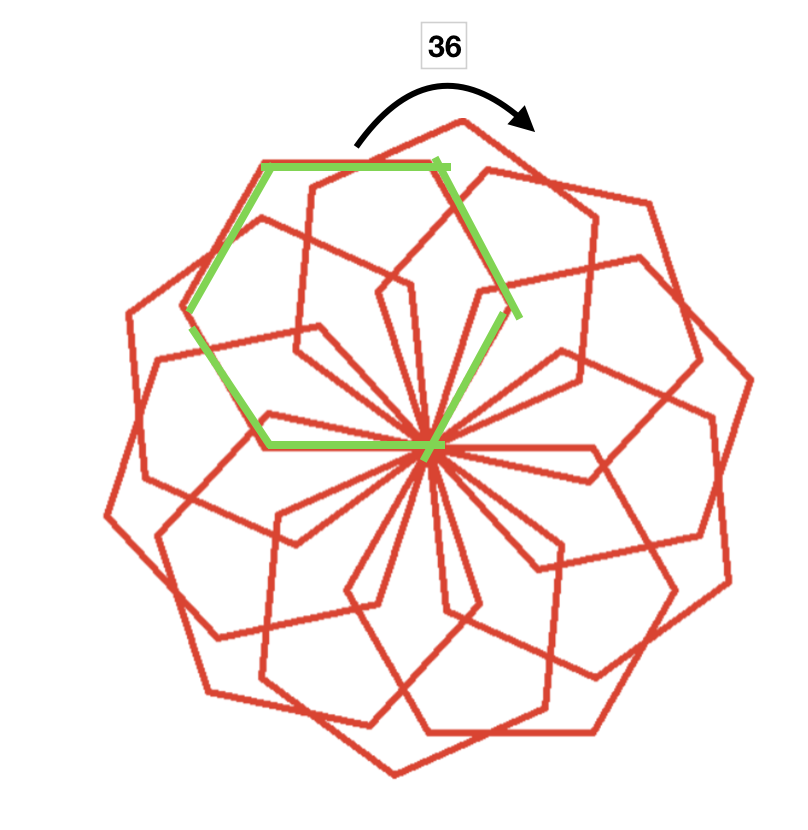
import turtle
for _ in range(6):
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.right(60)
import turtle
turtle.speed(0)
for _ in range(10):
for _ in range(6):
turtle.forward(100)
turtle.right(60)
turtle.right(36)
## Drawing a Pyramid of Dots
* Simple dots
#three dots
import turtle
size = 5
turtle.up()
for j in range(3):
turtle.dot(size)
turtle.forward(size*3)
turtle.hideturtle()

import turtle
size = 5
turtle.up()
for i in range(7):
for j in range(i):
turtle.dot(size)
turtle.forward(size*3)
turtle.goto(0, i*size*3)
turtle.hideturtle()

#three dots
import turtle
size = 5
turtle.up()
for i in range(7):
for j in range(i):
turtle.dot(size)
turtle.forward(size*3)
turtle.goto(0, -i*size*3)
turtle.hideturtle()
# http://10.c1021.fun

import turtle
size = 5
turtle.up()
for i in range(7):
for j in range(i):
turtle.dot(size)
turtle.forward(size*3)
turtle.goto(-i*size*3, -i*size*3)
turtle.hideturtle()
import turtle
size = 5
turtle.up()
for i in range(7):
for j in range(i):
turtle.dot(size)
turtle.forward(size*3)
turtle.goto(-i*size*3/2, -i*size*3)
turtle.hideturtle()
# Print with end
for i in range(5):
print(i)
for i in range(5):
print(i, end=":")
for i in range(5):
print(i, end=" OK ")
print("")
for i in range(5):
print("*", end="")

# Five star
for i in range(1, 6):
for j in range(i):
print ('* ', end="")
print('')

n=5;
for i in range(n,0,-1):
for j in range(i):
print('* ', end="")
print('')

n=5;
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i):
print ('* ', end="")
print('')
for i in range(n,0,-1):
for j in range(i):
print('* ', end="")
print('')
# Can you do with one loop?
for i in range(11):
for j in range(i):
print ('* ', end="")
print('')
# Can you do with one loop?
for i in range(11):
jj = i
if i>5:
jj = 10 - i
for j in range(jj):
print ('* ', end="")
print('')
## Python magic: str * input
print("hi" * 5)
print("* " * 3)
```
#
# #
# # #
# # # #
# # # # #
```
# Five star
for i in range(1, 6):
print ('# ' * i)

# Seven pyramind
for i in range(8):
print(" " * i, end = "")
for j in range(i):
print ("* ", end="")
print('')
# Seven pyramind
for i in range(8):
print(" " * (7-i), end = "")
for j in range(i):
print ("* ", end="")
print('')
# Seven pyramind with str * int
for i in range(8):
print(" " * (7-i), end = "")
print ("* " * i)
# Lists and Tuples
* After completing this presentation, you are expected to be able to:
* Manage a collection of things using a list or a tuple in Python
* Explain the major difference between lists and tuples
* Create a two dimensional structure using lists or tuples
## Dealing with scores
* Three student scores: 91, 80, 99.
* print their scores
* find the max and min scores
s1 = 91
s2 = 80
s3 = 99
print(s1, s2, s3)
# Find max
# Find min
## 7 Student Scores
* 92, 96, 89, 78, 99, 88, 100
* print, find max, find min
* sorting
* change it to letter grade
* ...

score = [92, 96, 89, 78, 99, 88, 100]
print("length", len(score))
print("score 0", score[0])
print("score 3", score[3])
print("score 8", score[8])
score = [92, 96, 89, 78, 99, 88, 100]
length = len(score)
for i in range(0, length):
print(score[i])
# Find MAX
score = [92, 96, 89, 78, 99, 88, 100]
length = len(score)
# put a small number
max = 0
for i in range(0, length):
if score[i] > max:
max = score[i]
print("Max score is", max)
http://pythontutor.com/iframe-embed.html#code=%23%20Find%20MAX%0Ascore%20%3D%20%5B92,%2096,%2089,%2078,%2099,%2088,%20100%5D%0Alength%20%3D%20len%28score%29%0A%0A%23%20put%20a%20small%20number%0Amax%20%3D%200%0A%0Afor%20i%20in%20range%280,%20length%29%3A%0A%20%20if%20score%5Bi%5D%20%3E%20max%3A%0A%20%20%20%20max%20%3D%20score%5Bi%5D%0A%0Aprint%28%22Max%20score%20is%22,%20max%29&codeDivHeight=400&codeDivWidth=350&cumulative=false&curInstr=0&heapPrimitives=nevernest&origin=opt-frontend.js&py=3&rawInputLstJSON=%5B%5D&textReferences=false
score = [92, 96, 89, 78, 99, 88, 100]
for s in score:
print(s)
# Find MAX
score = [92, 96, 89, 78, 99, 88, 100]
# put a small number
max = 0
for s in score:
if s > max:
max = s
print("Max score is", max)
# Find Min
score = [92, 96, 89, 78, 99, 88, 100]
for s in score:
print("min score is", )
## List Exercises
* Find avg
* Find median value
* If there is an even number of observations, then there is no single middle value; the median is then usually defined to be the mean of the two middle values.
* More list exercises at https://www.w3resource.com/python-exercises/list/
## The Range Command
* The range command creates a range of numbers
* Make a range of numbers between 1 and 5 using the following code:
`range(1, 6)``
* Returns a range of numbers which includes 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
print(list(range(1, 6)))
print(list(range(5, 10))) # 5 to 9 (5 inclusive, but 9 exclusive)
print(list(range(1, 11))) # 1 to 11 (1 inclusive, but 11 exclusive)
print("default start is 0")
print(list(range(10)))
print("Step size is 2")
print(list(range(0, 10, 2)))
print(list(range(1, 10, 2)))
print("Step size is 3")
print(list(range(0, 10, 3)))
## More examples
print(list(range(-1,-10,-2)))
print(list(range(10, 1)))
print(list(range(-10, 1,-1)))
print(list(range(-10, 1, 1)))
print(list(range(-10, 1, 0)))
## For Loops
```
for item in a list of items :
. . .statement(s). . .
```
* You need to give a list of items to a for loop
* This is where the range command is commonly used
* prints out a list of four numbers:
* The end value means a space is put at the end of the number when it is printed, instead of moving to the next line
`print(i, end=" ")`
for i in range(4):
print(i, end=" ")
## Excercises
* Print odd nemers from 0 to 100
* Print numbers from 0 to 100 but not multiple of 3
* 0 1 4 5 7 8 10 11 13 ...
for i in range( ):
print(i, end=" ")
## Using a ‘Fixed’ List in a For Loop
* For loop is an iterator or any given list, `[1, 4, -4, 2]`
* We can make a string list, `["apple", "banana", "cherry"]`
for i in [1, 4, -4, 2]:
print(i, end=" ")
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for fruit in fruits:
print("I like", fruit)
## Nested for loops
# Example from w3school
adj = ["red", "big", "tasty"]
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for a in adj:
for f in fruits:
print(a, f)
## Using a String in a For Loop
* A string will be changed into a list of letters automatically when it is used in a for loop
* String "Wild hair" becomes
`["W","i","l","d"," ","h","a","i","r"]`
for i in "This is Sung!":
print(i, end="*")
## Excercise
* Replace `s` to `x`
for i in "This is Sung!":
if i is 's':
print('x', end="")
else:
print(i, end="")
## More examples
* https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-list/
## Break and Continue
* https://www.programiz.com/python-programming/break-continue



# Use of break statement inside loop
for s in "lovesung":
if s == 's':
break
print(s)
print("The end")
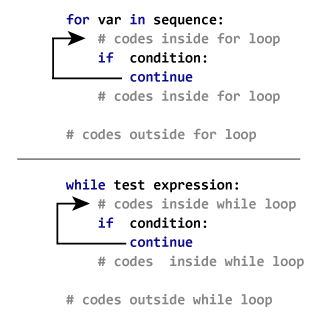
# Use of continue statement inside loop
for s in "lovesung":
if s == 's':
continue
print(s)
print("The end")
# Prime using for
sum = 0
for i in range (2, 100):
is_prime = True
for j in range(3, i):
if i%j == 0:
is_prime = False
if is_prime:
print("Prime: ", i)
sum = sum + i
print("Sum = " , sum)
## More Excercise
* Add 1 to 100
* Add even numbers from 10 to 1000
* Add two spaces between words
* Reverse string
* Write prime number sum using `if` and `break`
* Rewrite the turtle race using for loops